The Luminous Solar System
As you look up at the night sky, have you ever wondered about the vast and mysterious solar system that surrounds us? The solar system, consisting of the sun and the celestial objects that orbit around it, is a fascinating topic that has intrigued scientists and enthusiasts for centuries. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the solar system, exploring its components, characteristics, and the relationship between them.

The Sun: Our Luminous Star
At the center of the solar system lies the sun, a luminous star that provides the light and heat necessary for life on Earth. The sun’s massive size and gravitational pull exert a dominant force on the solar system, shaping the orbits of the planets that revolve around it. From its fiery core to its outer layers, the sun’s structure is a complex and dynamic system that influences the behavior of all the celestial bodies in its vicinity.
The Planets: Our Enigmatic Neighbors
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune – these are the eight planets that make up our solar system. Each planet has its own unique characteristics, such as size, composition, atmosphere, and distance from the sun. From the rocky terrain of Mercury to the gaseous clouds of Jupiter, the planets offer a diverse and fascinating look at the various environments that exist in our solar system.
The Inner Planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars
The inner planets, also known as the terrestrial planets, are Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. These planets are characterized by their solid surfaces and relatively small sizes compared to the gas giants. Mercury, the closest planet to the sun, is a barren world with extreme temperature fluctuations. Venus is a hot and toxic planet with a dense atmosphere that traps heat, making it the hottest planet in the solar system. Earth, our home planet, is a unique oasis of life with its moderate temperatures and abundance of water. Mars, the fourth planet from the sun, is a cold and dusty world known for its rusty red color and potential for hosting life.
The Outer Planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune
The outer planets, also referred to as the gas giants, are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. These planets are characterized by their massive size, ring systems, and gaseous compositions. Jupiter, the largest planet in the solar system, is a stormy world with a turbulent atmosphere and a prominent Great Red Spot. Saturn is known for its beautiful ring system made up of icy particles and rocky debris. Uranus and Neptune are colder and more distant from the sun, with unique characteristics such as tilted axes and icy compositions.

This image is property of mvsolar.in.
The Dwarf Planets: Pluto and Beyond
In addition to the eight planets, there are also dwarf planets that exist in the outer regions of the solar system. Pluto, once classified as the ninth planet, is now considered a dwarf planet due to its relatively small size and eccentric orbit. Beyond Pluto, there are other dwarf planets such as Eris, Haumea, and Makemake that orbit the sun in the Kuiper Belt. These dwarf planets provide valuable insights into the diversity of celestial bodies that populate the outer regions of our solar system.
Moons: The Silent Guardians
Moons are natural satellites that orbit planets and dwarf planets in the solar system. These celestial bodies come in various sizes and shapes, ranging from small rocky moons to large icy worlds. Moons play a crucial role in the dynamics of their parent planets, influencing tides, weather patterns, and geological processes. Earth’s moon, for example, is responsible for the ocean tides that occur on our planet. Jupiter’s moon Europa is believed to have a subsurface ocean that could harbor life. Moons provide a fascinating glimpse into the complex interactions that exist within the solar system.

This image is property of i.pinimg.com.
Asteroids and Comets: Cosmic Wanderers
Asteroids and comets are small rocky or icy bodies that roam the solar system, tracing elliptical orbits around the sun. Asteroids are rocky remnants from the early solar system, ranging in size from small boulders to massive dwarf planets. Comets, on the other hand, are icy bodies that originate from the outer regions of the solar system and develop bright tails when they approach the sun. These cosmic wanderers provide clues about the formation and evolution of the solar system, shedding light on the processes that have shaped our celestial neighborhood.
The Kuiper Belt and Oort Cloud: Hiding Places of Celestial Objects
The Kuiper Belt and Oort Cloud are vast regions of icy debris that lie beyond the orbit of Neptune, extending far into the outer reaches of the solar system. The Kuiper Belt is home to icy bodies such as Pluto and Eris, while the Oort Cloud contains a reservoir of comets that occasionally visit the inner solar system. These regions serve as hiding places for celestial objects that have played a significant role in the evolution of the solar system, providing valuable insights into its history and composition.
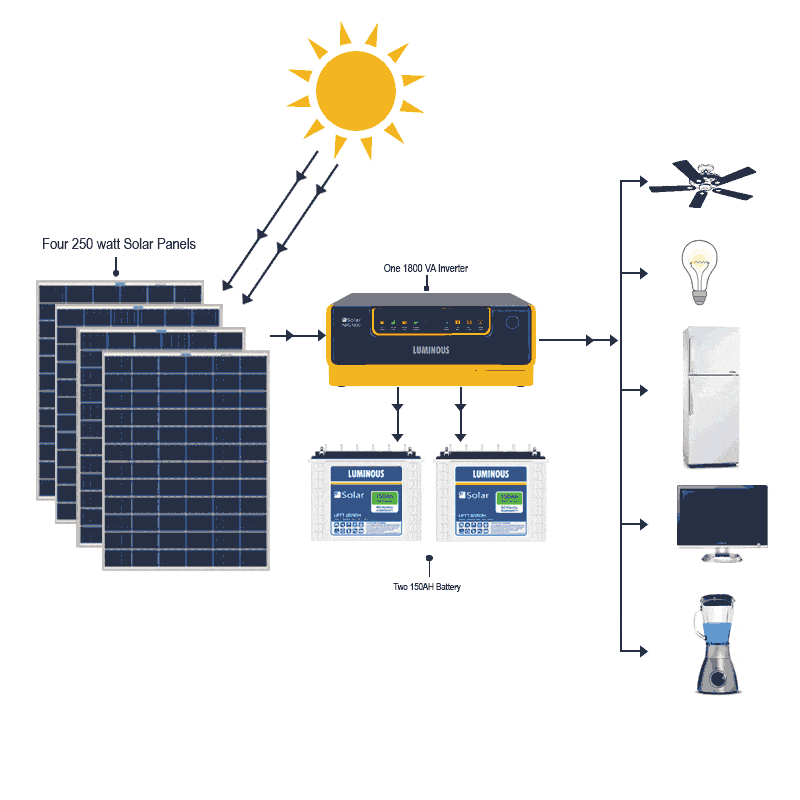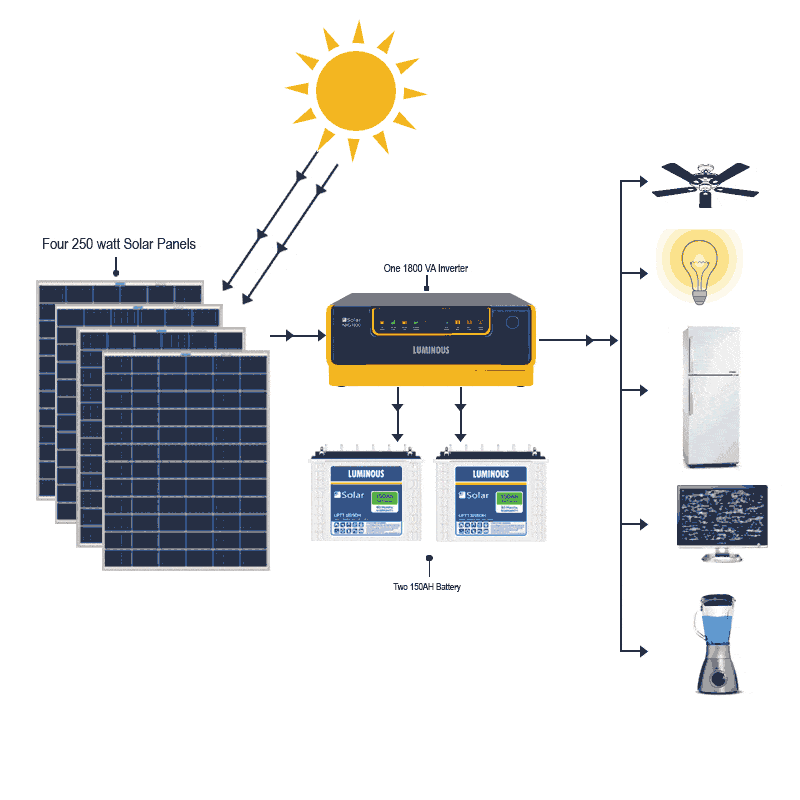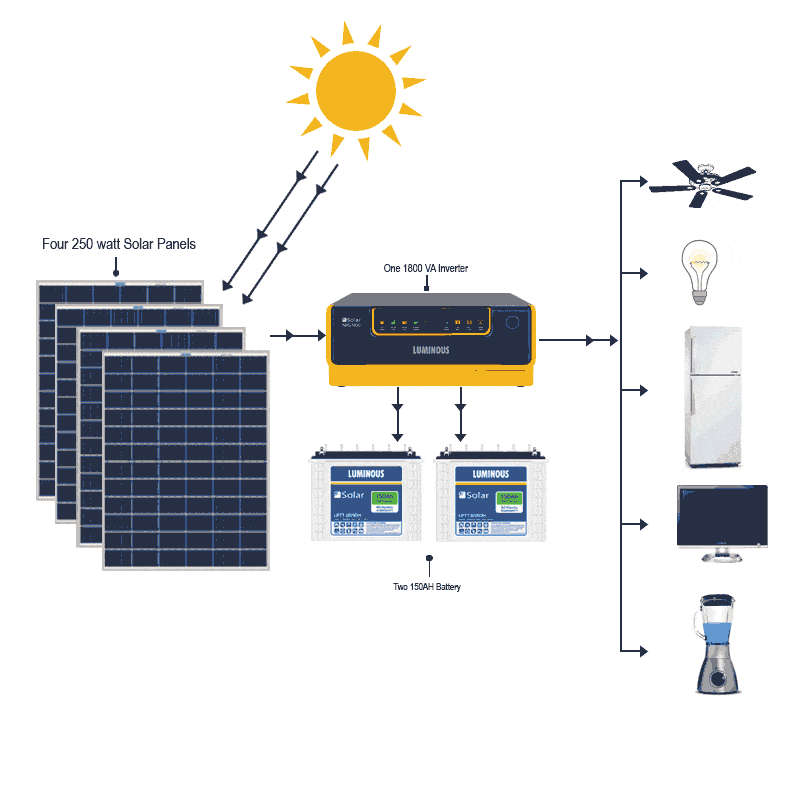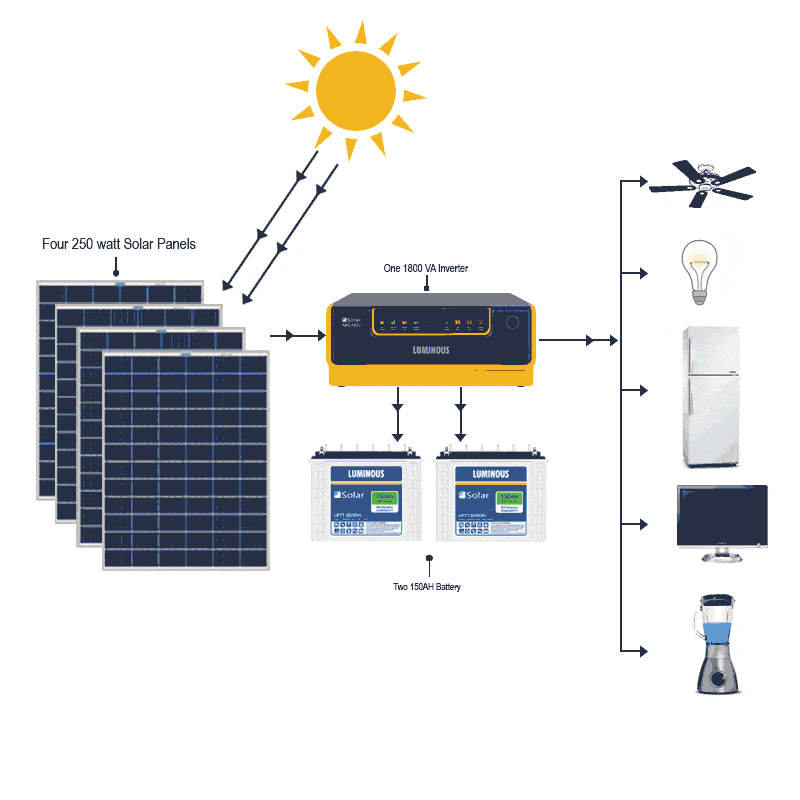
This image is property of kenbrooksolar.com.
Solar System Exploration: Unraveling the Mysteries
Over the years, scientists have conducted numerous missions to explore the solar system and uncover its many mysteries. From the first spacecraft to visit Mercury to the probes that have landed on Mars, planetary exploration has provided valuable data and images that have revolutionized our understanding of the solar system. Missions like the Voyager spacecraft and the Hubble Space Telescope have brought us stunning views of distant planets, moons, and asteroids, expanding our knowledge of the vast cosmos that surrounds us.
In conclusion, the solar system is a dynamic and wondrous tapestry of celestial bodies that captivate the imagination and inspire curiosity. From the blazing light of the sun to the icy depths of the Kuiper Belt, each component of the solar system plays a unique role in the grand cosmic ballet that unfolds before our eyes. By studying the planets, moons, asteroids, and comets that populate our solar system, we gain a deeper appreciation for the beauty and complexity of the universe in which we live. As we continue to explore and unravel the mysteries of the solar system, we embark on a journey of discovery that opens new horizons and expands our understanding of the cosmos.